Embracing the metaverse signifies an exciting frontier for businesses. The essence of real-time scene rendering through 3D Gaussian splatting is pivotal in crafting an immersive metaverse, enhancing the way we interact and conduct business in virtual realms. This groundbreaking method holds the promise of creating rich, navigable 3D scenes, a core component of a thriving business metaverse.
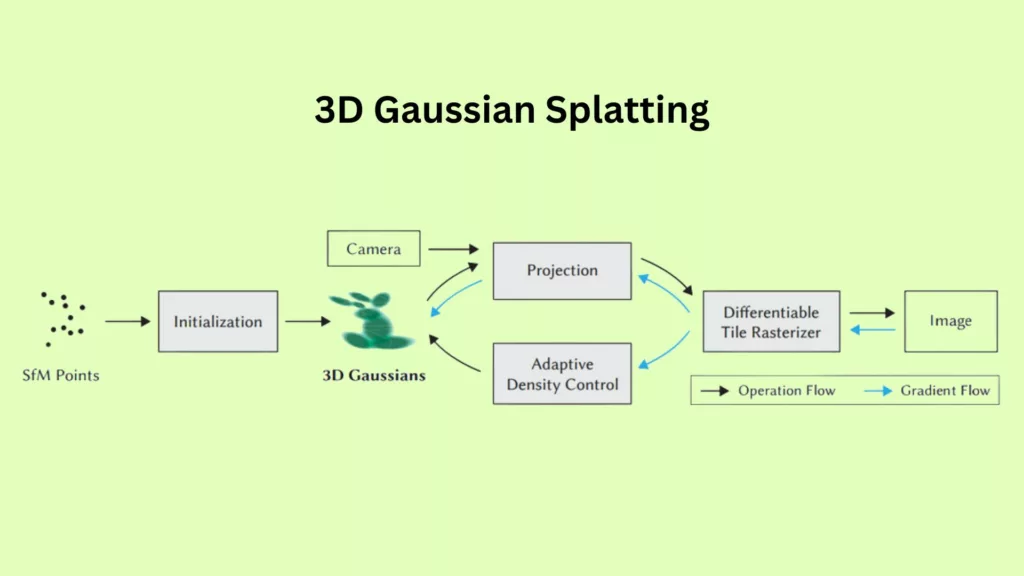
The journey commences with the assimilation of a sparse point cloud, embodying the geometry of the envisioned scene. This is achieved through the art of structure-from-motion (SfM), employing a medley of scene images captured from varied vantage points to ascertain the 3D coordinates of points within the scene. The ensuing step is the illumination representation within the scene, which is where the magic of Gaussian splatting comes to play.
The Gaussian function, with its characteristic bell-shaped curve, becomes an instrumental agent in depicting the scene’s light. By positioning a Gaussian function at each juncture in the point cloud, and through a meticulous process of optimization, the size and form of the Gaussian functions are finely tuned to encapsulate the scene with utmost precision. This entails honing the optimal parameters for each Gaussian function, such as its position, size, and intensity, ensuring a meticulously accurate representation.
Armed with this representation, rendering new images of the scene from diverse viewpoints becomes a breeze. Employing a swift tile-based renderer, the light perceived from each pixel in the image is rapidly calculated, projecting the Gaussian functions onto a 2D plane and fusing them to manifest the final image. The upshot is a real-time rendering apparatus capable of exhibiting high-resolution images of complex 3D scenes at interactive frame rates.
3D Gaussian splatting is not merely a method; it’s a gateway towards a business metaverse where real-time interaction with 3D environments is paramount. It’s about transcending traditional business models and stepping into a realm where virtual reality shapes the future of business interactions and operations in the metaverse.